The hazards of air pollution experienced by humans were primarily the hazards to human health at first, and then gradually discovered various hazards to industrial and agricultural production and adverse effects on weather and climate. People’s in-depth research on the mechanism, distribution, and scale of air pollutants has provided the necessary basis for the control and prevention of air pollution. After air pollution, due to the different sources, nature, concentration, and duration of pollutants, the differences in the meteorological conditions of the polluted areas, the differences in the geographical environment and other factors, and even the differences in people’s age and health conditions, they will cause different harms to each person.
The impact of air pollution on the human body is first to feel uncomfortable, then physiologically reversible, and then further appear acute hazard symptoms. The harm of air pollution to humans can be roughly divided into three types: acute poisoning, chronic poisoning, and carcinogenesis.
(1) Acute poisoning
When the concentration of pollutants in the air is low, it usually does not cause acute human poisoning, but under certain special conditions, such as special accidents in the production process of the factory, a large number of harmful gases leaking out, and sudden changes in external meteorological conditions, etc., It will cause acute poisoning of the crowd. For example, the leak of methyl isocyanate from the Pabor Pesticide Plant in India directly harmed the human body, causing 2,500 deaths and more than 100,000 victims.
(2) Chronic poisoning
The chronic toxic effect of air pollution on human health is mainly manifested in the phenomenon of increased prevalence of pollutants after they act on the human body continuously for a long time at a low concentration. The incidence of lung cancer among urban residents in China is very high, with the highest rate in Shanghai, where respiratory diseases are significantly higher among urban residents than in the suburbs.
(3) Carcinogenicity
This is the result of long-term effects, because pollutants act on the body for a long time, damage the genetic material in the body, and cause mutations. If the germ cells are mutated, the offspring will have various abnormalities, which is called teratogenicity; if it causes the organism’s cell inheritance The effect of sudden changes in material and genetic information is also called mutagenicity; if it induces tumors, it is called carcinogenicity. The “cancer” referred to here includes benign tumors and malignant tumors. Carcinogens in the environment can be divided into chemical carcinogens, physical carcinogens, and biological carcinogens. The process of carcinogenesis is quite complicated, and there are generally initiation stages and prolongation stages. Factors that can induce tumors are collectively referred to as carcinogenic factors. Tumors caused by long-term exposure to carcinogenic factors in the environment are called environmental tumors. Air pollution will lead to a decline in human life.
Air pollutants are mainly divided into harmful gases (carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, photochemical smog, halogen elements, etc.) and particulate matter (dust and acid mist, aerosols, etc.). Their main sources are factory emissions, automobile exhaust, land reclamation, forest fires, cooking smoke (including roadside barbecues), dust (including construction sites), etc.
Solutions to air pollution from factories can be roughly divided into three important links. The steps are from the waste gas collection, to waste gas treatment equipment and process purification, and then to the end gas detection and then to the atmosphere from the chimney.
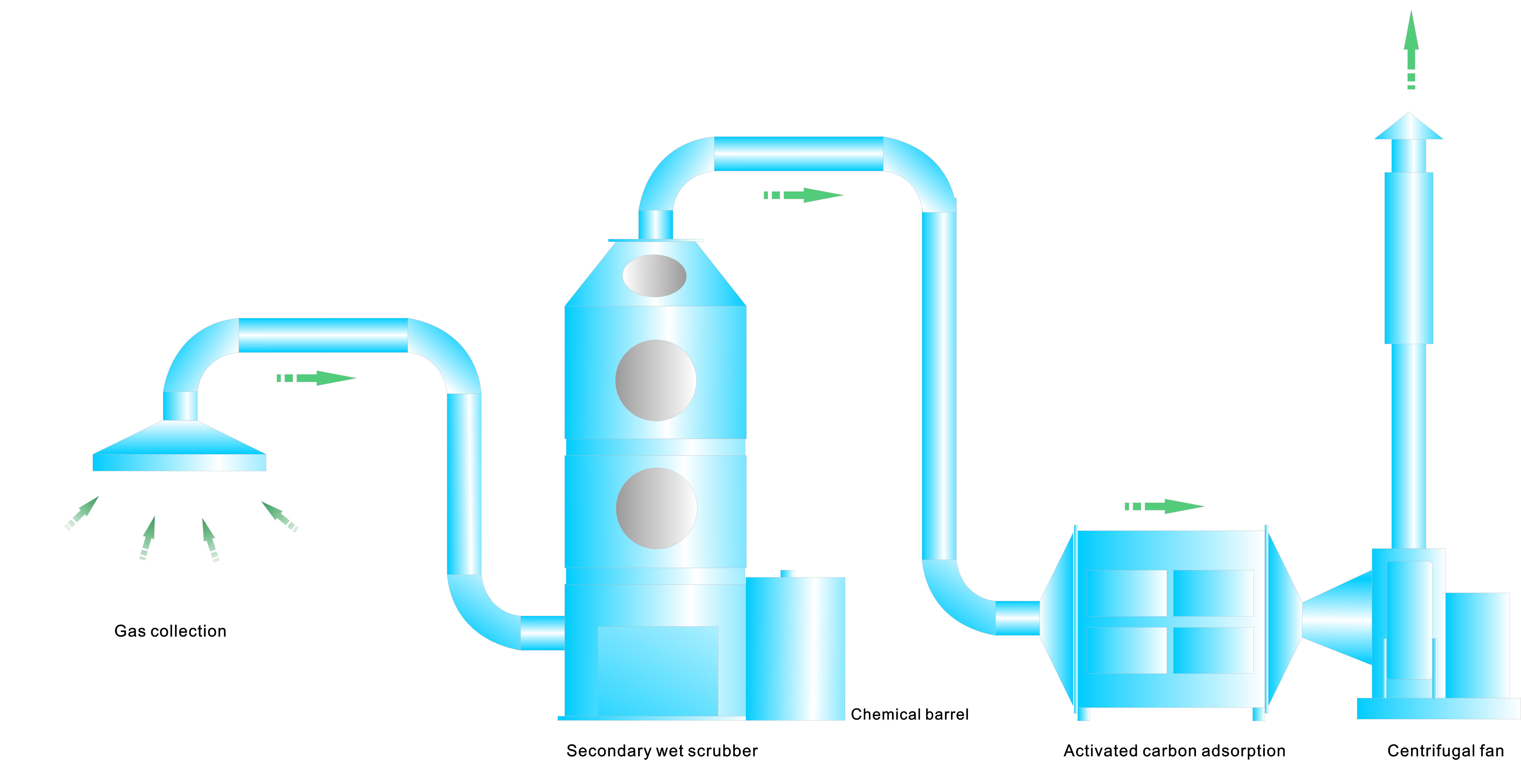
1. Exhaust gas collection
At each pollution source point of the factory’s exhaust gas emission, according to the actual production conditions of the working conditions, select the appropriate side-suction or top-suction exhaust gas suction hoods, and connect them with the air ducts one by one to form a complete exhaust gas collection system. Exhaust gas is collected under power.
Due to different waste gas treatment processes, before waste gas collection, consider whether the composition of the waste gas discharged by the factory is complex and whether the waste gas of different natures is collected by classification, so as to facilitate the purification of the terminal waste gas to meet the standards.
2. Selection of waste gas treatment equipment and purification process
After understanding the exhaust gas composition, concentration, and exhaust volume value of the factory’s emission, first, determine the exhaust gas treatment process, and then purchase the exhaust gas treatment equipment from the manufacturer.
In the vacant part of the factory area, the installation site is selected according to the size of the waste gas treatment system, and then the ground is leveled and cement hardened, and the equipment can be installed after entering the factory.
Or consult an environmental protection company, explain the parameters of the factory’s exhaust gas, and then provide the exhaust gas treatment solution, and then purchase the corresponding exhaust gas treatment equipment from the manufacturer according to the requirements of the exhaust gas process design.
Contact the environmental protection engineering company. If the company’s qualifications meet the requirements, they will install waste gas treatment equipment at the designated waste gas treatment site until the equipment is installed, and then debug and operate.
3. Exhaust emission detection
Finally, there is the exhaust gas detection link, which will affect or affect whether the exhaust gas emitted by the factory is purified, whether the gas detection at the chimney outlet meets the standard, and whether it meets the emission requirements of the national J or local environmental protection departments. Exhaust emission detection is divided into offline detection and online monitoring. Most small and medium-sized enterprises are offline monitoring. The installation requirements of online monitoring are determined by the national environmental protection department according to the nature, scale, and exhaust characteristics of different industries.