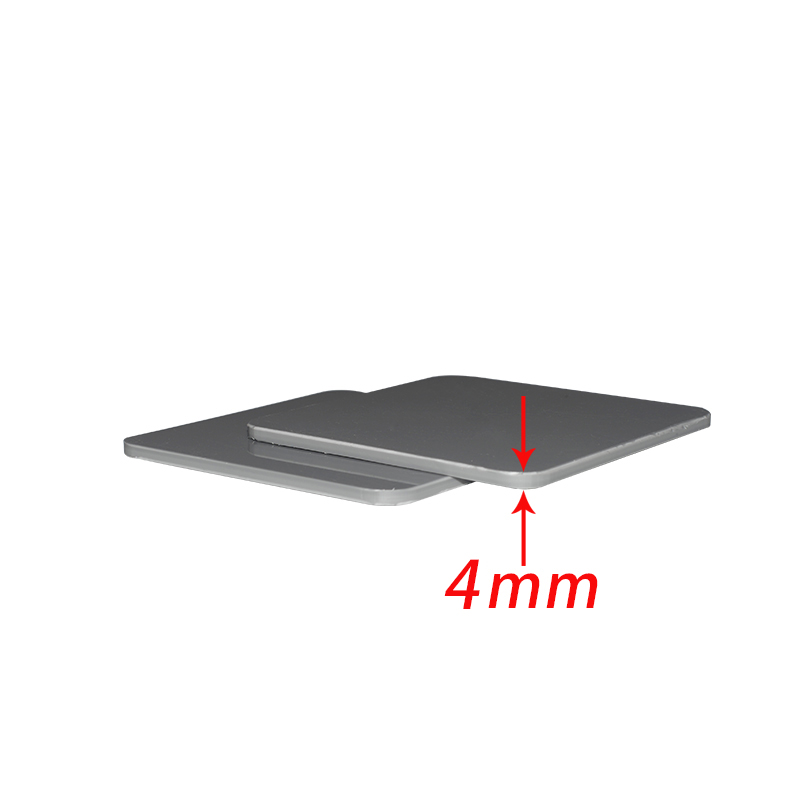
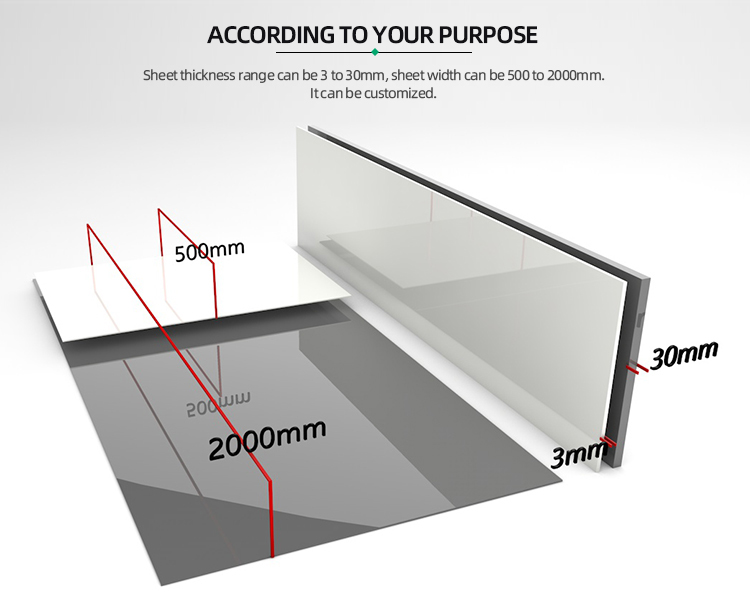
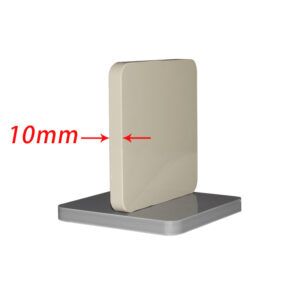
Description
Polypropylene PP is a semi-crystalline material. It is deeper than PE and has a higher melting point. Since the homogeneous PP sheet becomes brittle and easy to break when the temperature is lower than 0℃, many commercial PP sheets add 1~4% ethylene raw material to improve the flexibility of the sheet.The strength of polypropylene PP increases with the increase of ethylene content. The melting point temperature of polypropylene is 150°C. Due to the increased crystallinity, the board surface and scratch-resistance of this material are very good. PP board is usually used in a corrosion-resistant environment, and the PP is improved by adding glass fiber, metal additives, or thermoplastic rubber.

The flow rate MFR range of polypropylene sheet is 1-40. PP materials with low MFR have lower impact resistance but lower elongation strength. The shrinkage rate of PP is quite high, 1.8~2.5%. And the directional uniformity of shrinkage is much better than that of PE-HD materials. Adding 30% of glass additives can reduce the shrinkage to 0.7%. Both type and fluid type PP materials have excellent moisture absorption, acid and alkali resistance, alkali resistance, and solubility resistance. However, it does not melt at high temperatures like PE for PP boards such as gasoline (such as benzene) solvents and industrial hydrocarbons (carbon tetrachloride) solvents.